6 Reasons To Use Safari Over Google Chrome on iPhones, Macs
Safari browser Vs Google Chrome: Apple is significantly enhancing user privacy with its Safari browser, surpassing Google Chrome. The company has outlined several features designed to keep users safe in their daily browsing activities.
)
Apple has launched a campaign highlighting six key areas where their browser, Safari, protects user privacy. These areas include combating cross-site tracking, shielding location data, securing extensions, and offering enhanced Private Browsing with link protection.

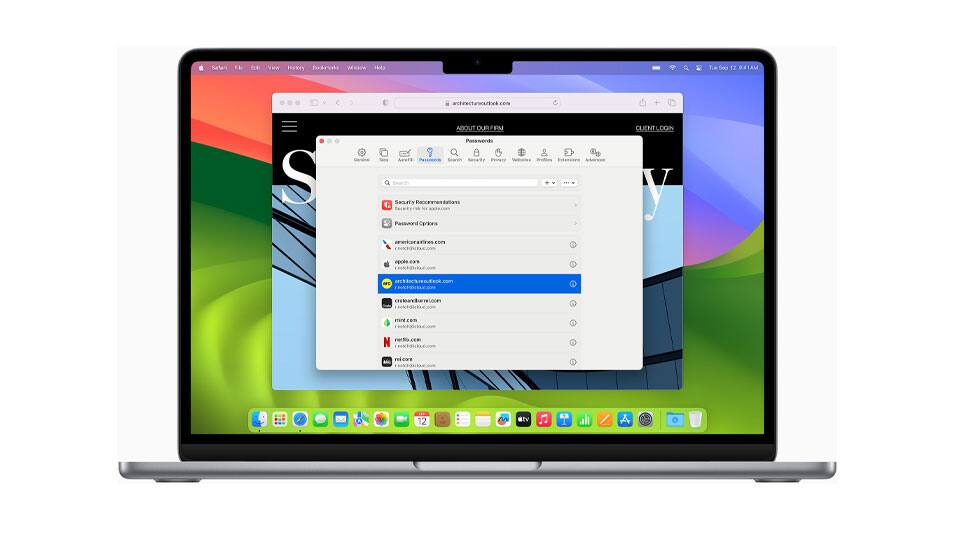
Private Browsing in Safari prevents the browser from saving the web pages visited, searches made, or AutoFill information. Apple strengthens these protections with Face ID and Touch ID.

Apple has implemented Intelligent Tracking Prevention, a feature that uses machine learning to identify and isolate domains used for tracking users. This feature, enabled by default in Safari, continuously evolves to block new tracking techniques.

Safari hides users’ IP addresses from known trackers, preventing them from identifying users across websites and sessions and revealing precise locations.

Safari removes unnecessary trackers appended to URLs shared in Messages and Mail, as well as those in Private Browsing mode. This helps maintain user privacy while browsing.
Safari helps protect location data by not sharing it with any search engine and giving users control over whether to share location information with websites. Users can choose to share or not, or remember their decision for one day.
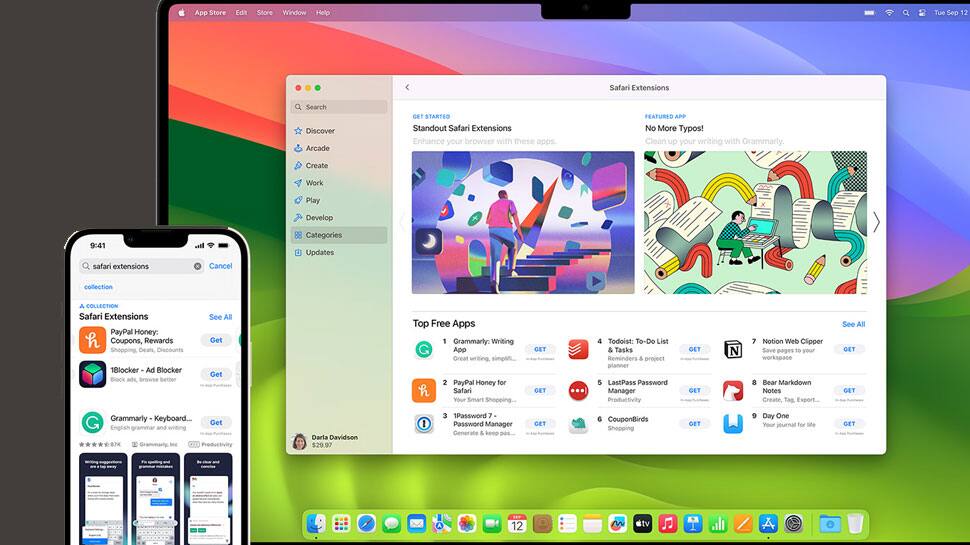
Safari informs users about the information web extensions can access before they enable them, unlike some extensions in other browsers that may track on-screen activities.

