7 Surprising Disadvantages of Consuming Too Many Onions
)
Consuming too many onions can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and stomach cramps. Onions contain fructans, a type of carbohydrate that may be difficult to digest, particularly for individuals with sensitive stomachs or conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
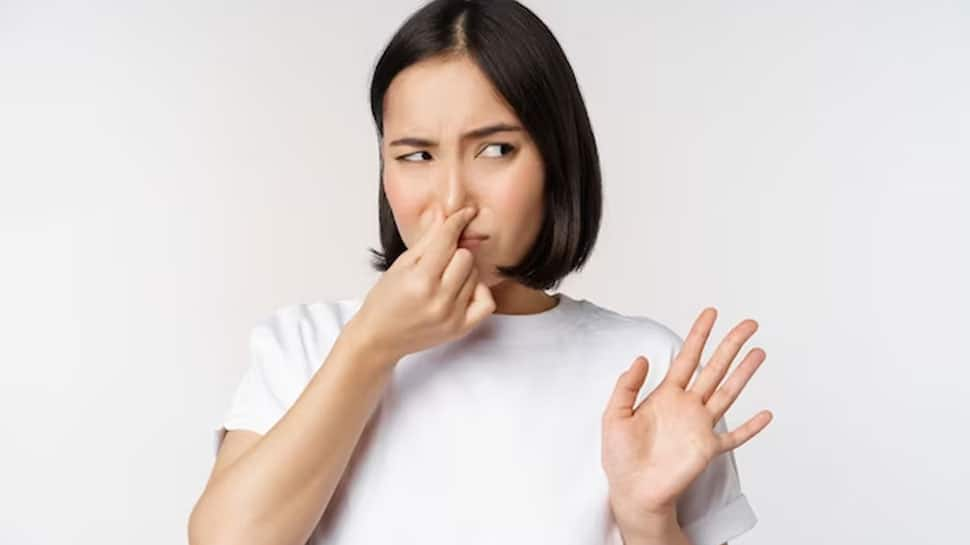

Onions, especially when eaten raw, can cause bad breath due to their high sulfur content. The odor lingers even after brushing, as sulfur compounds are absorbed into the bloodstream and released through the lungs, leading to persistent unpleasant breath.
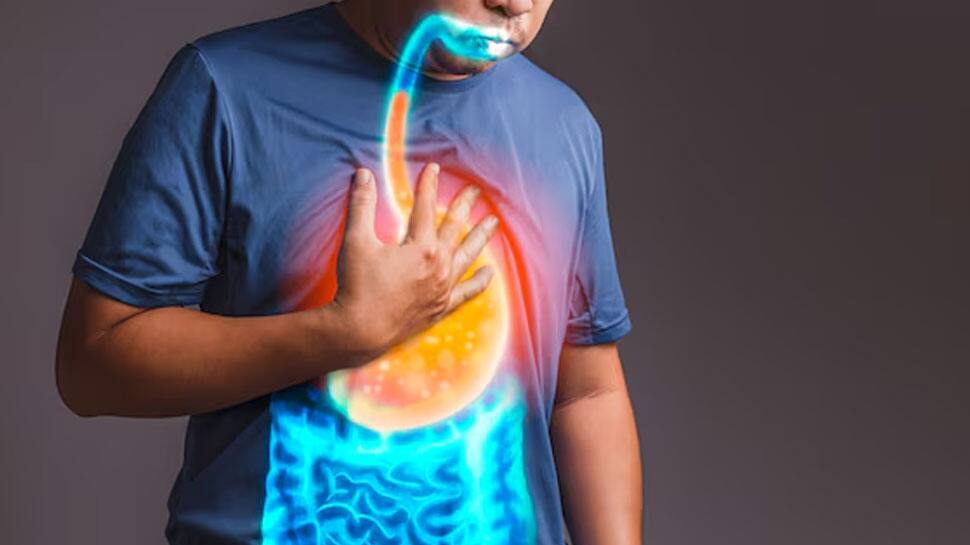
Overconsumption of onions can trigger or worsen acid reflux in some individuals. Onions are acidic and can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and discomfort.
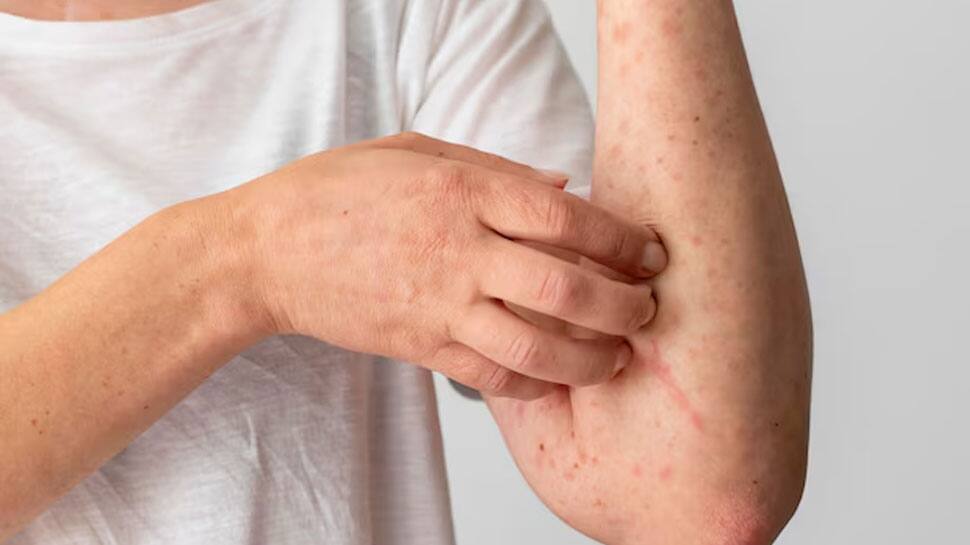
Some people may experience allergic reactions to onions, which can manifest as skin rashes, itching, swelling, or respiratory issues. Consuming onions in excess could heighten the severity of these allergic symptoms in sensitive individuals.
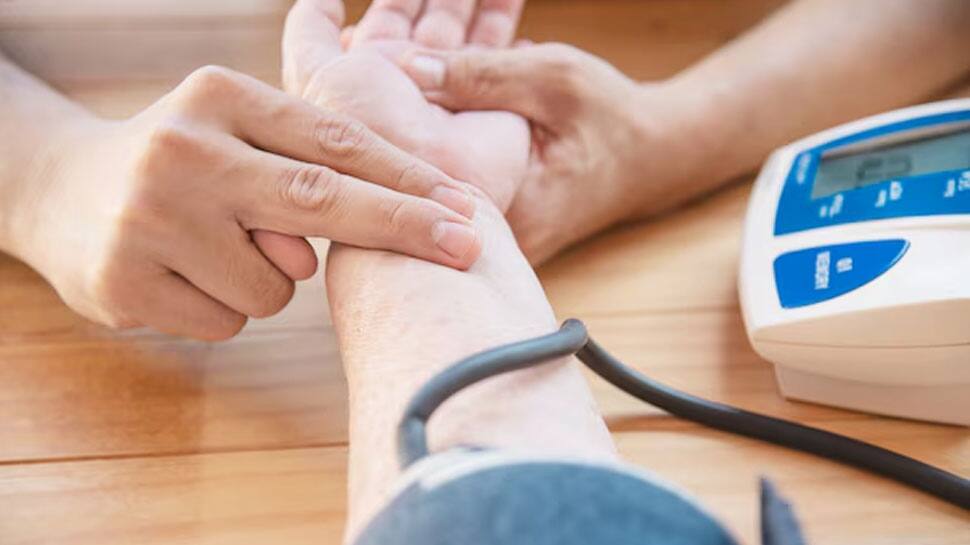

Onions have natural blood-thinning properties, which can lower blood pressure. While this is beneficial in moderation, excessive consumption may lead to dangerously low blood pressure levels, especially for individuals already on blood pressure medications.
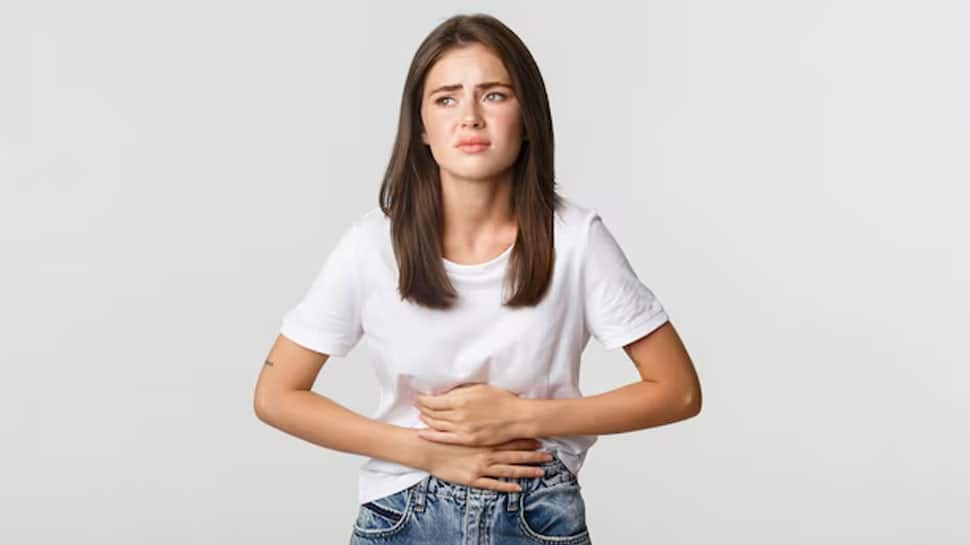

Onions are rich in fiber and fermentable carbohydrates, which can increase gas production in the intestines. This can result in excessive flatulence and bloating, particularly when onions are consumed in large quantities.
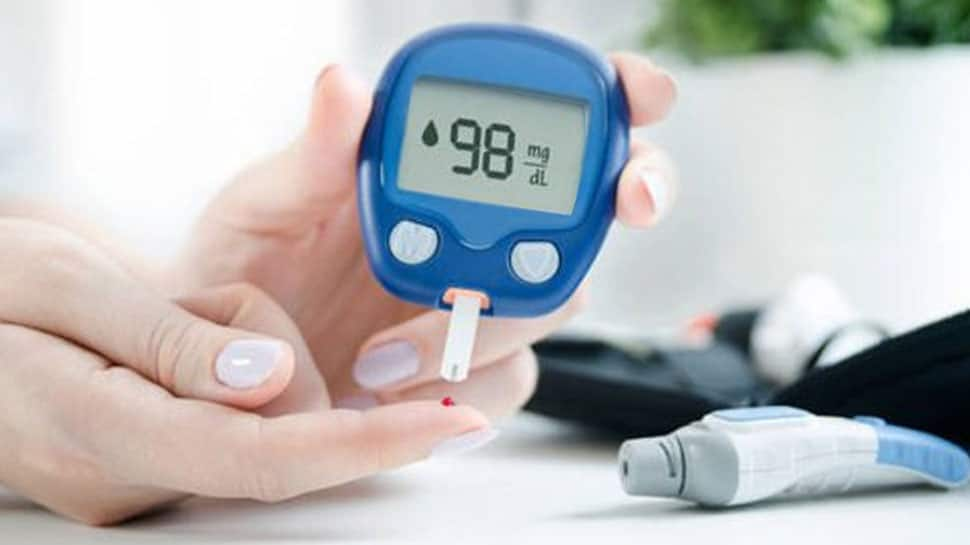
While onions can have a mild blood sugar-lowering effect, consuming too many may interfere with blood sugar regulation, especially for diabetics. In some cases, excessive intake may complicate blood sugar management, requiring adjustments to medications or diet.
(This photo gallery is meant for informational purposes only and must not be considered a substitute for advice provided by qualified medical professionals.)

