Earth just got 2000 light-years closer to supermassive black hole in the centre of our galaxy
Did you know that Earth just got 7 km/s faster and about 2000 light-years closer to the supermassive black hole in the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy?
- Did you know that Earth just got 7 km/s faster and about 2000 light-years closer to the supermassive black hole in the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy?
- Here's what it means.
Trending Photos
)
In a new development in our universe, Earth just got 7 km/s faster and about 2000 light-years closer to the supermassive black hole in the centre of the Milky Way Galaxy.
According to Japanese space experts in National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), the changes are results of a better model of the galaxy based on new observation data.
NAOJ clarified that this doesn’t mean that our planet is plunging towards the black hole. The new observation data includes a catalogue of objects observed over the course of more than 15 years by the Japanese radio astronomy project VERA.
VERA (VLBI Exploration of Radio Astrometry, by the way, “VLBI” stands for Very Long Baseline Interferometry) started in 2000 to map three-dimensional velocity and spatial structures in the Milky Way.
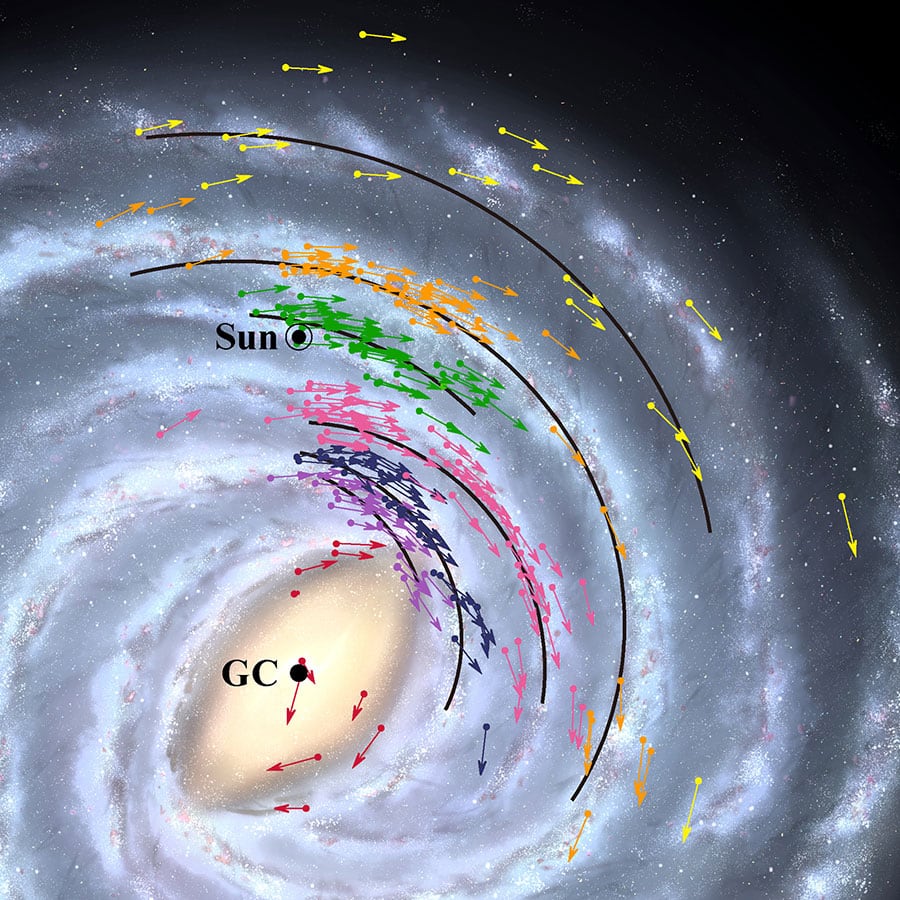
VERA uses a technique known as interferometry to combine data from radio telescopes scattered across the Japanese archipelago in order to achieve the same resolution as a 2300 km diameter telescope would have. Measurement accuracy achieved with this resolution, 10 micro-arcseconds, is sharp enough in theory to resolve a United States penny placed on the surface of the Moon.
As Earth is located inside the Milky Way Galaxy, we can’t step back and see what the Galaxy looks like from the outside, NAOJ said. Astrometry, accurate measurement of the positions and motions of objects, is a vital tool to understand the overall structure of the Galaxy and our place in it. This year, the First VERA Astrometry Catalog was published containing data for 99 objects.
Based on the VERA Astrometry Catalog and recent observations by other groups, astronomers constructed a position and velocity map. From this map, they calculated the centre of the Galaxy, the point that everything revolves around. The map suggests that the centre of the Galaxy, and the supermassive black hole which resides there, is located 25800 light-years from Earth.
This is closer than the official value of 27700 light-years adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1985. The velocity component of the map indicates that Earth is travelling at 227 km/s as it orbits around the Galactic Center. This is faster than the official value of 220 km/s.
Earth just got 7 km/s faster and 2000 light-years closer to the black hole in our galaxy. These changes are results of a better model of the #MilkyWayGalaxy based on observation data, including a catalog of objects observed by VERA.https://t.co/utBGj61Pexhttps://t.co/d04FhOrHJp pic.twitter.com/aPcPga7DM7 — NAOJ (@prcnaoj_en) November 26, 2020
Now VERA hopes to observe more objects, particularly ones close to the central supermassive black hole, to better characterizes the structure and motion of the Galaxy.
Stay informed on all the latest news, real-time breaking news updates, and follow all the important headlines in india news and world News on Zee News.
Live Tv







)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
